Geographical Information System
Geographical information
system (GIS) otherwise know as Geospatial information system is the system or techniques to create or
capture, store, analyze, manage and represent data with reference to real earth
coordinate. In other way, GIS is the combination of modern cartography (map
creation method), various statistical analysis and enterprise (Database)
technology. Before entering into the subject, there are some terminologies
which act as a speed breaker to proceed further and making confusion i.e. what
is Geographic Information? What kind of data it refers? What is a coordinate
system? etc. Geography comes from a
Greek word “Geographia”, which means Earth (Geo) and it’s Description. The
study of the Earth and its features present on it.
Eratosthenes was the first person to use the word
Geography (276-194 BC). Now we can go to an entity/feature/object on the earth
surface; a building, a bridge, a tree etc. which is occupying a space and
represents a location. Occupying a space is called spatial and the location is
represented with X Y coordinates. So location is nothing but the position of
the object on the earth surface. If we relate all the things together, we will
get the meaning of GIS for some extent.
GIS
was started in early 1858, but it gets its real boost after 100 years (around
1960) when the computer mapping application was started. At the end of the 20th
century, GIS is reached a milestone where geospatial data and mapping
applications are being made available via the World Wide Web. GIS is used and
opportunities in various field of Government, Forestry, Agriculture, Town
Planning, Geology, Archaeology, Demography, Costal Planning, Disaster
Management etc. Now days everybody easily access a map in their mobile phone
and identifying their location with respect to real Earth coordinate (GPS
Technology). Easily find out the street name and required information from the
map. This is nothing but part of GIS techniques. During Disasters, govt.
official easily identify the most vulnerable location so that they can easily
take action to mitigate the upcoming disaster. In sever cyclonic stroke, the
relief team easily identify the shelter location and shortest path (road way)
to reach at particular location. Not only GIS helps to prepare digital map for
viewing purpose but helps to store unlimited size of related information along
with the spatial data for analyze and application purpose. In an example of
hospital mapping, the city municipality wants to make such a map, where all the
private and govt. hospitals will be located. Other than that the information
like; How many doctors, number of beds, ICU facility, lab facility, ambulance facilities
etc. can be attached to each hospital. This information not only helpful to
general public but this will helpful to govt. for analysis purpose and
management purpose.
With
the above idea now we can make a definition that, GIS is a computerized
technique to create, store, retrieve, manage, edit and analyze of spatial data.
GIS allow us to store spatial as well as non spatial data. A land or a property
on the map is spatial data, but the information like owner name, location name,
road name, owner’s father name are no-spatial data which are related to the
land.
Data Representation
GIS data represents to real Earth objects such as
tree, bridge, roads, land parcel, elevation data, landmark, building etc. These
data classified into two categories; discrete objects and continuous fields. Discrete
is represented by well defined boundaries “vector” graphics (Point, Line &
Polygons) and continuous data reference to grid or raster data representing
surface data such as elevation. In this instance, the data can be any value,
positive or negative; sometimes referred to as real data.
Vector Data
Geometrical representation of spatial data is in
Point, Line & Polygon i.e landmarks or location of a place in represented by
a point, streams or roads are represented by line and parcels or landuse are
represented by area or polygon geometry.
Raster Data
Raster data is represented as grid of cells (pixel)
covering an area. Each cell or pixel contains the information as an attribute
with row and column number and color value. An example of raster data is a
scanned map, satellite image or aerial photographs. The size of a raster file
is larger than a vector file
.
GIS Vs Traditional Map Creation Techniques
Earlier Maps are prepared in Hardcopy format. The
process was very difficult to prepare a single map. The accuracy of any
location was always a question mark. It was take many days to trace various
objects on a map and again in single map only few information can be displayed.
But due to GIS mapping technology this kind of problem have been resolved. You
can store as many as data in a map. The major advantage of GIS are; easy for
display, easy to store, data security, more information, lesser time, high
accuracy, easy to analysis etc. For an example; in traditional paper map you
can able to view a road and its name. But through GIS what ever data you want
to store you can store like you can view a road along with name, its width,
length, when the road was last repaired, who was the contractor etc. So this
kind of information we can store through GIS which will helpful for further
developmental planning.
How a Map is Prepared in GIS?
There are various GIS software’s are available for
map creation and data analysis. These maps are prepared through digitization
(Tracing various objects) from Satellite imagery, Aerial photographs or other
maps. These sources are available in Raster format (i.e. .image, .jpeg, .tiff
etc.). Before digitizing any maps, the sources are georeferenced using GPS
(Global Positioning System) point. Generally the map creation in GIS is
involved through the following process;
i.
Georeferencing
of Source Map or Image
ii.
Image
interpretation and Digitization
iii.
Ground
Verification
iv.
Survey
and Data Incorporation
v.
GIS
Application
Georeferencing:
 Georeferencing is refers to defines the existence
of any object or map with respect to physical earth surface. This is based on
map projection or coordinate system. These techniques are used to create a
common base to display your map. Many of us are using Google Earth or Google
Map in our day to day life. It looks whole world in a single image with
continuity. But in reality there are thousands of images are used in Google
Earth with different resolution and different tiles. But these are
georeferenced, so you can able to see each location separately. If these are
not georeferenced, then all the images open at a single place and you can find
Georeferencing is refers to defines the existence
of any object or map with respect to physical earth surface. This is based on
map projection or coordinate system. These techniques are used to create a
common base to display your map. Many of us are using Google Earth or Google
Map in our day to day life. It looks whole world in a single image with
continuity. But in reality there are thousands of images are used in Google
Earth with different resolution and different tiles. But these are
georeferenced, so you can able to see each location separately. If these are
not georeferenced, then all the images open at a single place and you can find
Image interpretation and Digitization:
Image interpretation is a technique to recognize
various earth features on the satellite images or aerial photographs and
accurately digitize them. For a common man it is difficult to identify many of
the features from the satellite imagery. For example; Forest ,
Agricultural land, orchards etc. are looks green but all of them are mapped
separately. The most basic principles for image interpretation are: size,
shape, shadow, tone/color, texture, pattern, association and experience. These
elements are taken care during map digitization.
In the above images which image is easier to
identify objects? Obviously the objects in the aerial photographs are very
accurately identified. When you go for high resolution, the coverage of the
area will be less but data accuracy will be high and when you go for low
resolution, the data accuracy will be less but it will covered a bigger area. To
finding features in low resolution images is comparatively difficult to high
resolution images. Presently maximum landbase maps are prepared from high
resolution satellite images and aerial photographs for better analysis. Using
various GIS & CAD software, the earth features are captured in various
vector layers.
Ground Verification:
 The vector data captured from the different
sources are sent for the ground verification for the existence check. During
this process, the survey team take hard copy map or mobile pad (contain vector
data) with GPS devices. For any decision making, accuracy of the data is highly
required. For example; in hilly region or forest covered area, many roads are
unidentified or covered under tree or slope. Even some of them are captured by
mistake. If a road captured without its existence, then people will suffer when
they referred the map. So during ground verification the existence of the
captured feature in GIS is verified and same is marked for correction.
The vector data captured from the different
sources are sent for the ground verification for the existence check. During
this process, the survey team take hard copy map or mobile pad (contain vector
data) with GPS devices. For any decision making, accuracy of the data is highly
required. For example; in hilly region or forest covered area, many roads are
unidentified or covered under tree or slope. Even some of them are captured by
mistake. If a road captured without its existence, then people will suffer when
they referred the map. So during ground verification the existence of the
captured feature in GIS is verified and same is marked for correction.
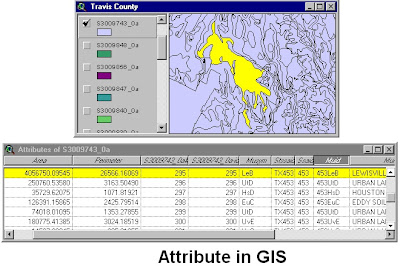
Survey and Data Incorporation:
 In GIS it is not only to represents the earth
features graphically but stored various data along with each features. For
example; if we map a building on a map, we can view the location name, owner of
the building, how many rooms, number of family members etc. which are store as
attribute along with the feature. Even we can link end number of data to a
feature from external database. Due to such facility it became easy to analyze,
planning for decision support. The information of data related to a feature is
collected through various sources. Survey method is the best way for data
accuracy and validation. Once the vector map is prepared in GIS environment,
the source maps are provided to survey team. They take such maps through hard
copy printouts or in mobile GIS (a device in which you can view your map with
limited editing facilities). Through this map, they collect the information as
required to full fill the purpose. These collected data may be in the form of
hardcopy sheets or in softcopy format. After completion of survey, such data
are stored in the respective features by manual data entry or through
automation tools in GIS environment.
In GIS it is not only to represents the earth
features graphically but stored various data along with each features. For
example; if we map a building on a map, we can view the location name, owner of
the building, how many rooms, number of family members etc. which are store as
attribute along with the feature. Even we can link end number of data to a
feature from external database. Due to such facility it became easy to analyze,
planning for decision support. The information of data related to a feature is
collected through various sources. Survey method is the best way for data
accuracy and validation. Once the vector map is prepared in GIS environment,
the source maps are provided to survey team. They take such maps through hard
copy printouts or in mobile GIS (a device in which you can view your map with
limited editing facilities). Through this map, they collect the information as
required to full fill the purpose. These collected data may be in the form of
hardcopy sheets or in softcopy format. After completion of survey, such data
are stored in the respective features by manual data entry or through
automation tools in GIS environment.
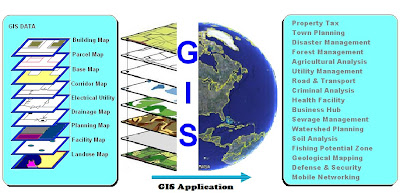
GIS Application:
Now days GIS is used in
every field of studies. This is involved from planning, observation and
collection of data to store and analysis of spatial data for decision making
process. GIS is both a database system with specific capabilities for spatially
referenced data, as well as a set of operation for working with data. GIS played as a key component in managing & maintaining
sustainable forest management. Terrain and ore body modeling, exploration,
drilling, mine planning, reclamation, and rehabilitation are important digital
mapping elements in mining industries. In power utility the process of routing
energy is highly dependent on geographic information. From network design to
outage management, more than 80 percent of utility data management contains
spatial components. Govt. used GIS for disaster prevention,
emergency response, and recovery & mitigation programs. Shortest path
analysis to provide relief, disaster shelter analysis and future planning are
include. All the computer educated persons are using Google Map to know the
location and required destinations. This also a part of GIS application for
general public to identifying any corner of the world in single click. So what ever field human can think, can
use GIS in better prospects.
***
To know more you can refer the below sites which
are help me to prepare this document;
1.
www.esri.com
3.
www.gis.com




No comments:
Post a Comment